Add suspense to your chord progressions with these augmented shapes
The music theory math is easy in this lesson, but can be devastatingly effective

An augmented chord is what we call a major chord with a raised (or sharp) 5th. You’ll hear it whenever the composer wants to set up a state of suspense, whether at the beginning of a song, as part of a chord progression, or in film scores to add a sense of foreboding at key moments.
As with many other aspects of music theory, there are actually a couple of different names that can be correctly used. I’ve already mentioned ‘sharp 5’, often notated as +5 in jazz chord charts, in the same school of shorthand as a minus sign being used for minor and a small circle for diminished. Check out a copy of the jazz ‘bible’ The Real Book to see these symbols in use.
Like any other chord, we can alter augmented to feature extensions such as the 7th. For example, Aaug7, or A7 (+5), which arguably makes things a bit clearer. It also gives you the essential harmony, plus any extensions in a format that might make reading a jazz chord chart on the fly less stressful!
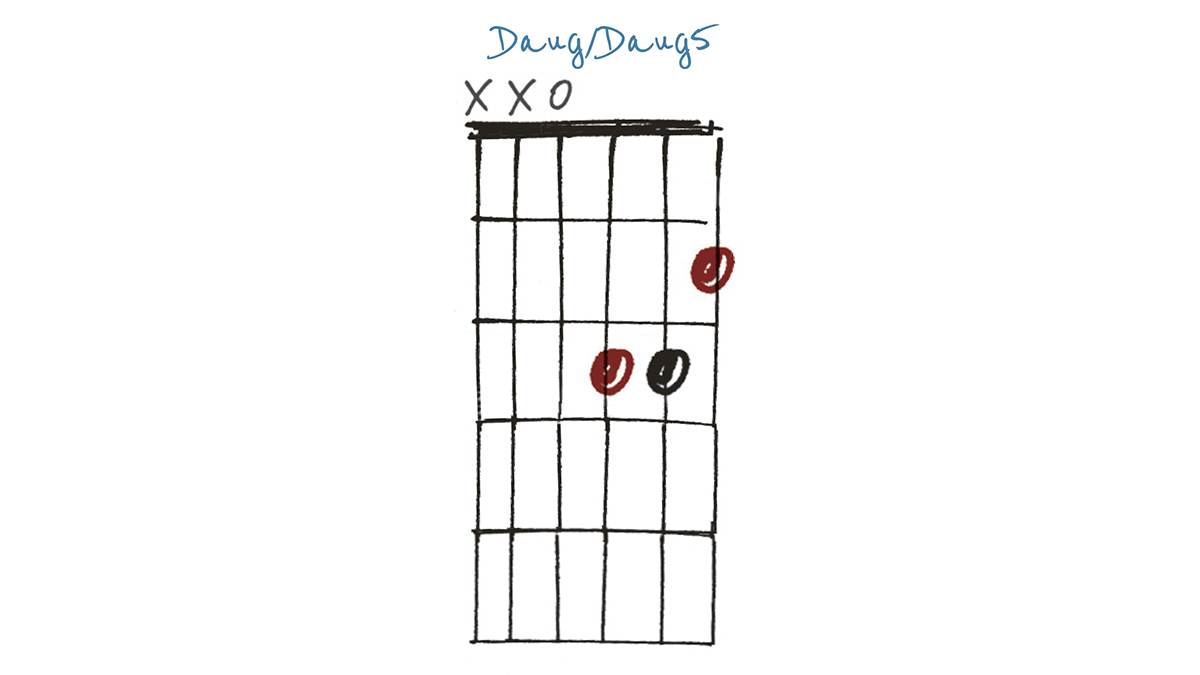
Example 1
This chord could correctly be referred to as D augmented, Daug5 or D (+5). The A# on the third string replaces the usual A, giving a sense of suspense not present in a regular D major. You could also alternate D major and D (+5), thereby recreating the intro to ABBA’s Mamma Mia.
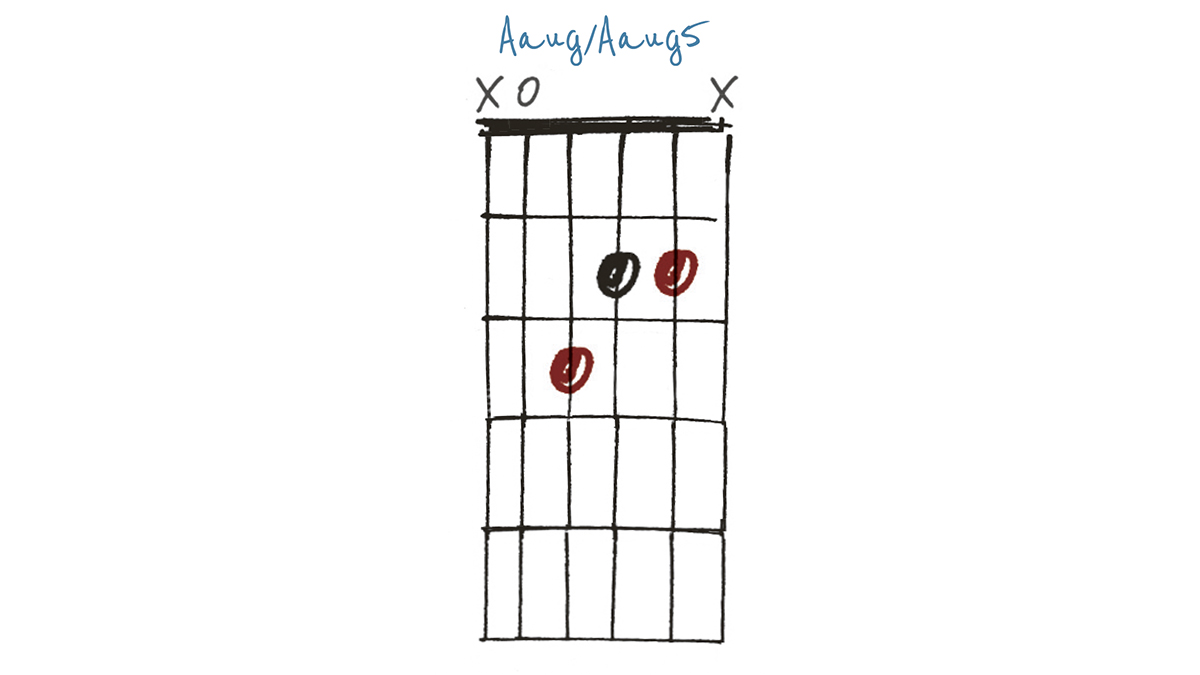
Example 2
Taking a regular open-position A major chord and raising the 5th (E) to F on the fourth string gives an A augmented, aka Aaug5 or A (+5). For a little extra spice in the high-end, you could allow the open top E string to ring, giving a non-augmented 5th. I suppose we could call that an A+add5…
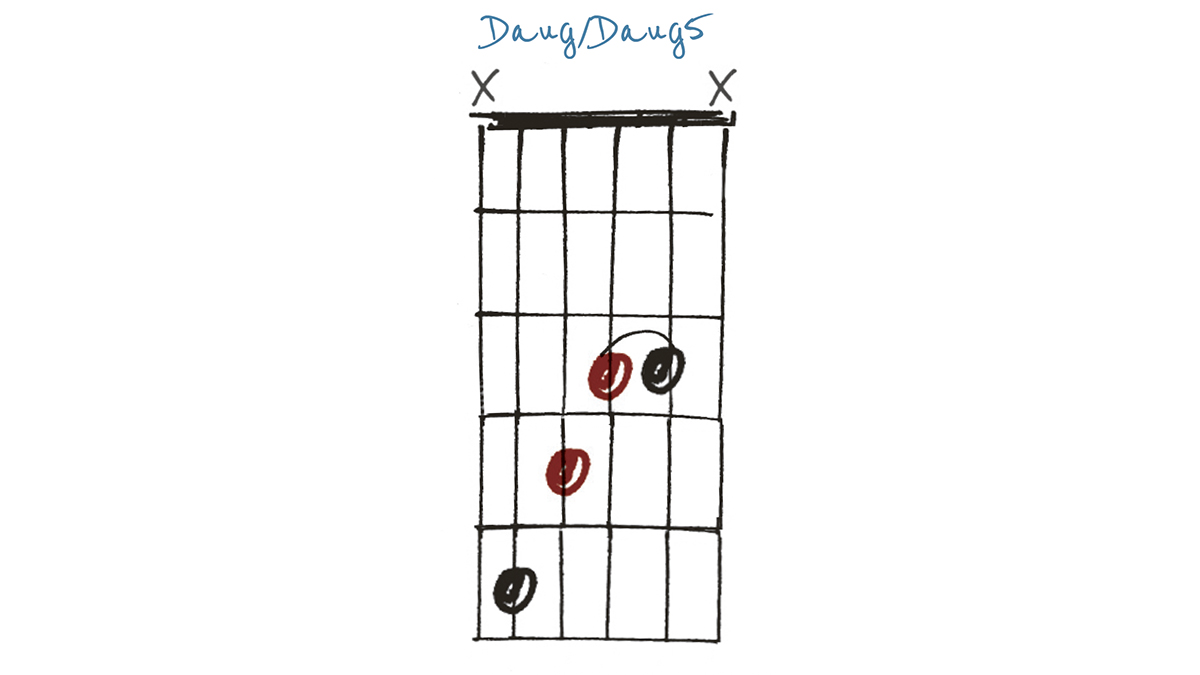
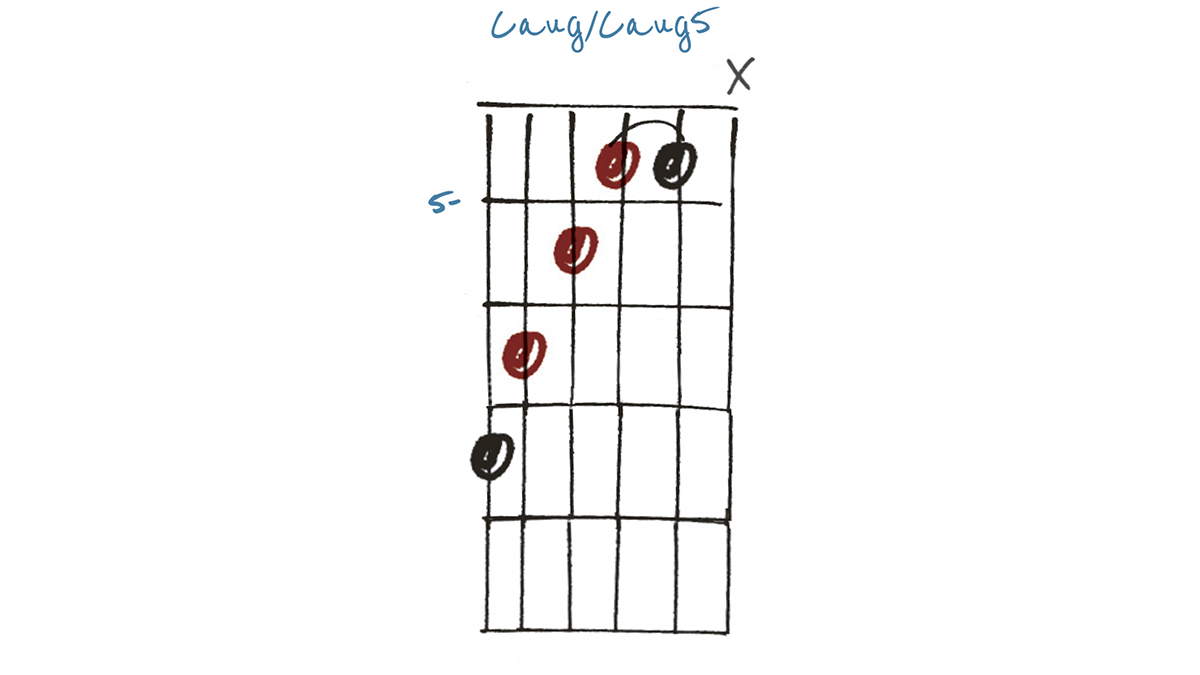
Example 3
Let’s just call this Daug5. It’s a lower, darker voicing but is technically the same chord as Example 1 and therefore interchangeable. Inversions such as these can be useful for creating chord/melody arrangements, or simply for adding a bit of variety when providing accompaniment to a soloist or singer.
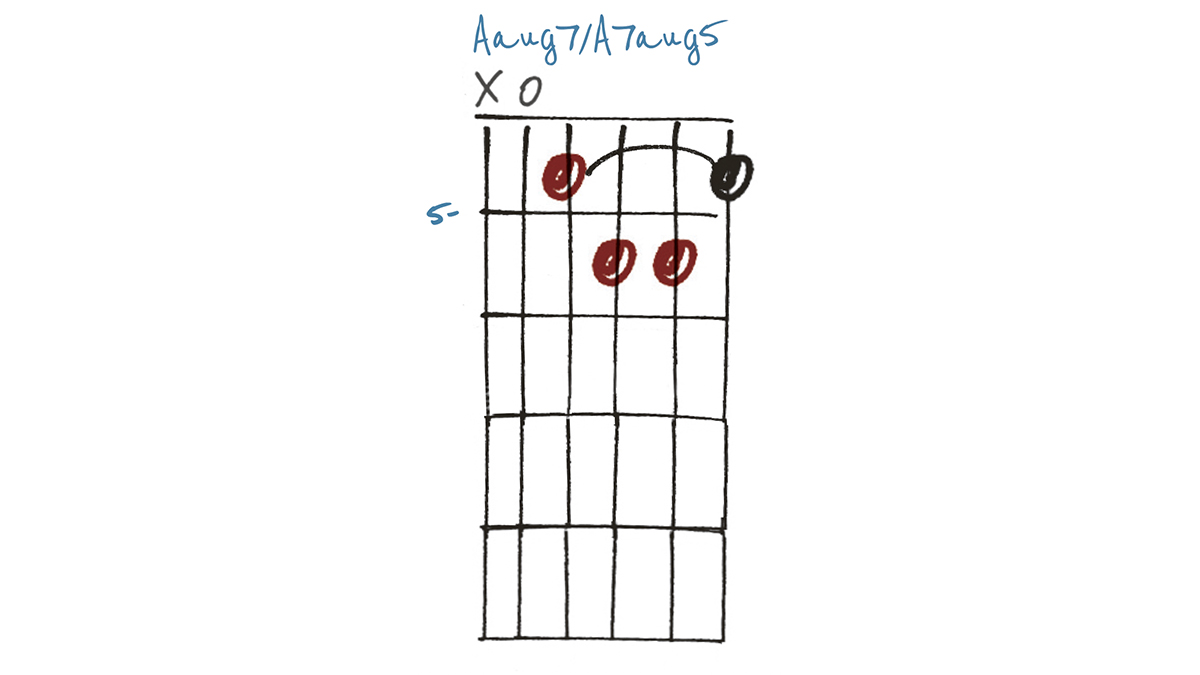
Example 4
Adding in a dominant 7th to this A (+5) chord gives us A7aug5. The aforementioned naming conventions remain correct, but rather than saying Aaug7, A7aug5 makes it clear what is going on harmonically – namely, that we’re sharpening/augmenting the 5th, and not the 7th.
All the latest guitar news, interviews, lessons, reviews, deals and more, direct to your inbox!
Example 5
This Caug5 is the lowest, darkest-sounding inversion, using the five lowest strings. It’s a bit of a stretch if you’re not used to it, but well worth the effort as it trains your fourth finger to be precise. Never a bad thing! You may also find this shape useful for ominous-sounding arpeggiated parts.
As well as a longtime contributor to Guitarist and Guitar Techniques, Richard is Tony Hadley’s longstanding guitarist, and has worked with everyone from Roger Daltrey to Ronan Keating.